
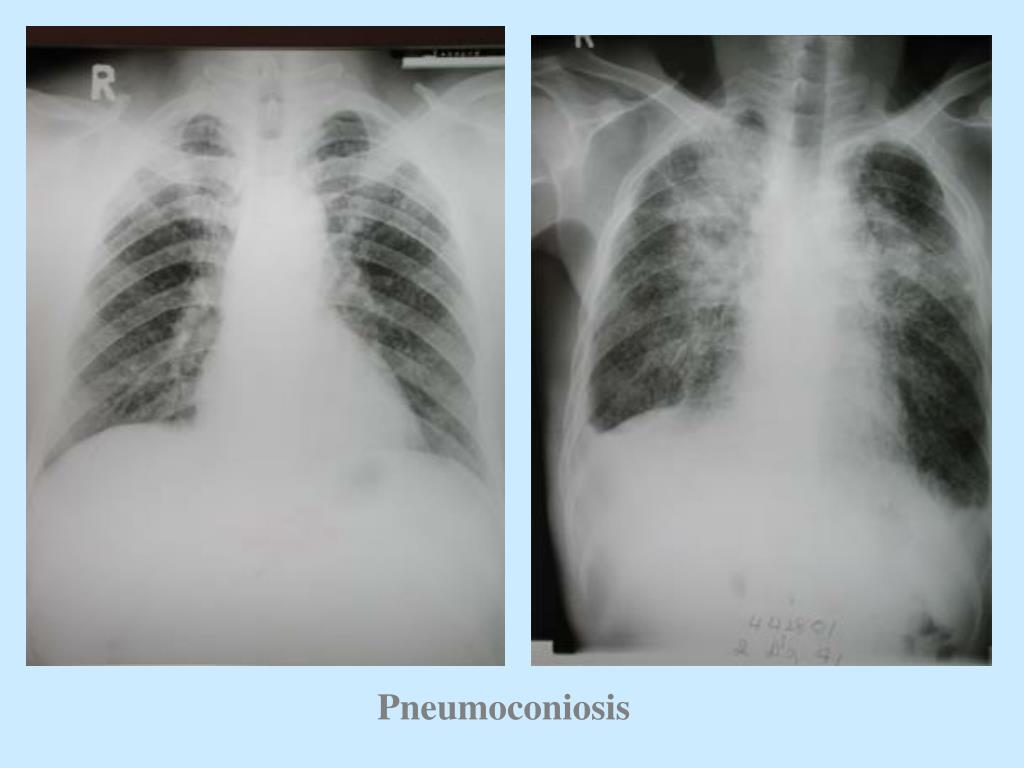
10 In this simplified system (META-PM classification), myopic maculopathy lesions are divided into 5 categories: “no myopic retinal lesions” (category 0), “tessellated fundus only” (category 1), “diffuse chorioretinal atrophy” (category 2), “patchy chorioretinal atrophy” (category 3), and “macular atrophy” (category 4). Recently, an international panel of myopia researchers reviewed previously published studies and classifications and proposed a simplified, uniform classification system for PM for use in future studies. A, Diffuse chorioretinal atrophy B, patchy chorioretinal atrophy C, lacquer cracks D, myopic CNV E, myopic CNV-related macular atrophy. 9 Characteristics of each lesion will be described in detail later. Myopic maculopathy includes diffuse chorioretinal atrophy, patchy chorioretinal atrophy, lacquer cracks, myopic choroidal neovascularization (myopic CNV), and CNV-related macular atrophy ( Fig. Pathologic myopia is defined as the presence of myopic maculopathy equal to or more severe than diffuse chorioretinal atrophy. This could enable a direct comparison between studies and finally could establish a systematic approach to prevent BCVA loss due to PM worldwide. These strongly suggest the necessity of a standardized definition of PM. In addition, staphyloma may be a cause of developing maculopathy and is not considered a lesion of myopic maculopathy. Thus, it seems difficult to diagnose staphyloma in 50-degree fundus photos. However, the most common type of staphyloma is a wide one beyond the 50 degrees of conventional fundus photos. 6–8 In these studies, myopic retinopathy was defined to include the following specific signs: posterior staphyloma, lacquer cracks, Fuchs spot, and myopic chorioretinal thinning or atrophy. In other studies, the presence of myopic maculopathy (sometimes called myopic retinopathy) was used to define PM. In most of the earlier epidemiological studies, refractive error or axial length (≥26.0 and ≥26.5 mm) or a combination of both was used to define “pathologic myopia.” However, a definition based on refractive error or increased axial length is considered to show just a “high degree of myopia.” In addition, there has been no clear evidence why these cutoff values were chosen. 1–5 However, the definition of PM has been inconsistent among studies. It has been reported that PM is a major cause of BCVA loss in the world, especially in east Asian countries. Pathologic myopia (PM) is different from other types of myopia in the sense that PM causes the loss of best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), not only the loss of uncorrected visual acuity. In the future, preventive therapies targeting staphyloma and eye deformity are expected before vision-threatening complications develop and it is too late for patients.
When ultra-widefield optical coherence tomography is available, it is expected to be a new tool that will surpass 3-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging is a powerful tool to analyze the entire shape of the eye. The mechanical load onto the important region for central vision (optic nerve and macula) is not comparable between eyes with and without posterior staphyloma. It is defined as an outpouching of the wall of the eye that has a radius of curvature that is less than the surrounding curvature of the wall of the eye.

Posterior staphyloma is unique to PM, except for inferior staphyloma due to tilted disc syndrome. Posterior staphyloma and eye deformity are important causes of developing vision-threatening complications.
On the basis of this study, PM has been defined as eyes having atrophic changes equal to or more severe than diffuse atrophy. The meta-analyses of the PM study group (META-PM study) made a classification system for myopic maculopathy. The main reason for best-corrected visual acuity loss is complications specific to PM, such as myopic maculopathy, myopic traction maculopathy, and myopic optic neuropathy (or glaucoma).

Pathologic myopia (PM) is the only myopia that causes the loss of best-corrected visual acuity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
